
Introduction of Montgomery Straps
Montgomery straps might sound like a term from a historical novel, but they are a vital tool in modern medicine. Often overlooked, Montgomery these simple yet effective devices play a crucial role in wound care, especially in post-surgical settings. Their significance lies not just in their utility but also in their ability to make wound management more efficient and less painful for patients. In this article, we will delve deep into what Montgomery straps are, their applications, benefits, and much more.
What are Montgomery Straps?
Montgomery straps have adhesive strips used primarily to secure dressings on wounds, particularly in situations where frequent dressing changes have required. They consist of two parts: adhesive tabs that have affixed to the skin around the wound and ties that hold the dressing in place. This design allows healthcare providers to change the dressings without repeatedly removing and reapplying tape, which can damage the skin.
Historical Background and Evolution
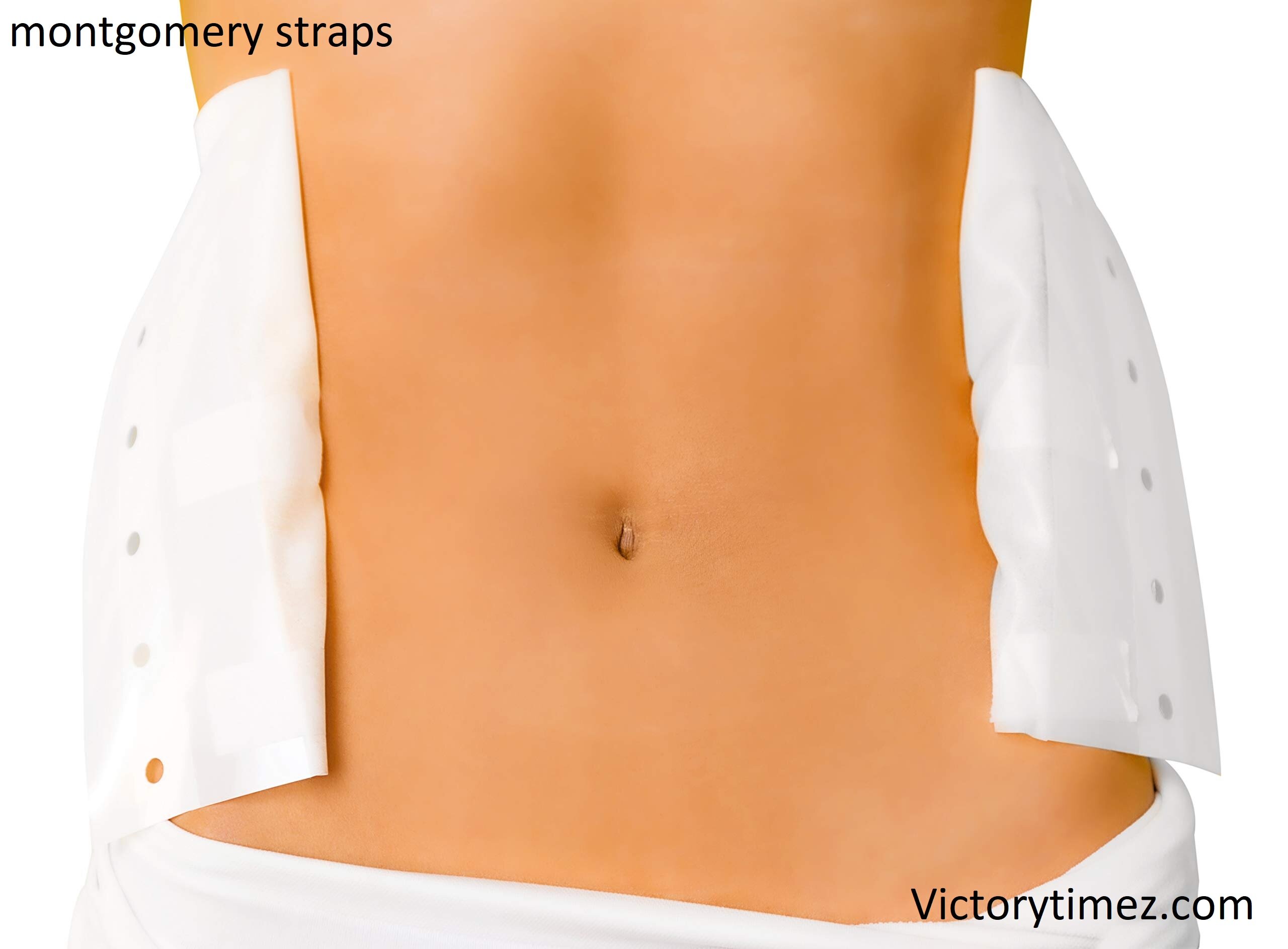
The concept of Montgomery straps dates back to earlier times when the need for a more patient-friendly wound care solution became apparent. Over time, as medical technology advanced, these straps have evolved from rudimentary designs to the more sophisticated versions used today.
Purpose of Montgomery Straps
The primary purpose of Montgomery straps is to secure wound dressings without causing skin trauma. This is particularly important in patients with fragile skin, such as the elderly or those with chronic conditions. By using Montgomery straps, healthcare providers can avoid the repetitive application of adhesive tapes, which can lead to skin tears or irritation.
Role in Wound Management
Montgomery straps are especially useful in managing wounds that require frequent inspection or dressing changes. They provide a stable and secure method to keep dressings in place, reducing the risk of infection and promoting better healing.
Preventing Skin Damage
One of the significant advantages of Montgomery straps is their ability to prevent skin damage. Traditional adhesive tapes can cause problems, especially in patients with sensitive skin. Montgomery straps minimize these risks by reducing the need for frequent tape application.
Types of Montgomery Straps
Montgomery straps come in various forms, each designed to meet specific needs. Understanding the different types can help in choosing the right one for each patient.
Traditional Montgomery Straps
The traditional design features simple adhesive strips with ties. These are easy to apply and remove, making them a popular choice in many medical settings.
Modern Variants and Innovations
In recent years, innovations in material science have led to the development of advanced Montgomery straps. These newer versions may include hypoallergenic materials, antimicrobial properties, or even designs tailored for specific types of wounds.
Materials Used in Montgomery Straps
The materials used in Montgomery straps are crucial to their effectiveness. Here’s a look at some of the common materials and their pros and cons.
Common Materials
Most Montgomery straps have made from medical-grade adhesives and fabrics. The adhesive part has typically made from materials like silicone, which is gentle on the skin. The fabric used for the ties is usually breathable, preventing moisture buildup.
Pros and Cons of Different Materials
While traditional materials are effective, they may not be suitable for all patients. For instance, some may have allergies to certain adhesives. In such cases, alternative materials like hypoallergenic adhesives or softer fabrics may be preferred.
Application of Montgomery Straps
Proper application of Montgomery straps is essential for them to function correctly. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Clean the Area Around the Wound: Before applying the straps, ensure the skin around the wound is clean and dry.
Apply the Adhesive Tabs: Place the adhesive tabs on either side of the wound, ensuring they are secure but not too tight.
Secure the Dressing: Place the dressing over the wound and tie the straps to hold it in place.
Adjust as Necessary: Ensure the dressing is secure but not causing discomfort to the patient.
Best Practices for Application
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying Montgomery straps. Regularly check the straps to ensure they remain secure and adjust them as needed to prevent discomfort or skin irritation.
Advantages of Using Montgomery Straps
Montgomery straps offer numerous benefits, both for patients and healthcare providers.
Benefits for Patients
For patients, the main advantage is comfort. Montgomery straps reduce the need for repeated tape application, which can be painful and damaging to the skin. They also make it easier to keep the wound area clean, which is crucial for healing.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
For healthcare providers, Montgomery straps simplify the process of wound management. They make dressing changes quicker and more efficient, allowing for better patient care.
Challenges and Considerations
While Montgomery straps are generally beneficial, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Potential Issues with Usage
Improper application of Montgomery straps can lead to problems such as skin irritation, slippage, or even infection if the wound has not properly covered.
How to Overcome Common Problems
To avoid these issues, ensure that the straps have applied correctly and that the wound has regularly monitored for signs of infection or irritation.
Montgomery Straps in Various Medical Conditions
Montgomery straps have used in a wide range of medical conditions, from post-surgical care to chronic wound management.
Use in Post-Surgical Care
In post-surgical care, Montgomery straps have often used to secure dressings over large incisions. This allows for easy inspection of the wound without disturbing the dressing.
Use in Chronic Wound Management
For chronic wounds, such as pressure ulcers or diabetic foot ulcers, Montgomery straps can help maintain a stable environment for healing while reducing the risk of further skin damage.
Comparing Montgomery Straps with Other Wound Care Options
While Montgomery straps are effective, they are not the only option available. Here’s a comparison with some alternatives.
Alternatives to Montgomery Straps
Alternatives include traditional adhesive tapes, self-adherent dressings, and negative pressure wound therapy. Each has its pros and cons, depending on the wound type and patient needs.
Pros and Cons of Different Options
Montgomery straps offer the advantage of easy dressing changes, but they may not be suitable for all wound types. Traditional tapes may provide a stronger hold but can damage the skin. Self-adherent dressings are easy to apply but may not provide as secure a fit as Montgomery straps.
Patient Comfort and Montgomery Straps
Patient comfort has a key consideration in wound care, and Montgomery straps have designed with this in mind.
How They Enhance Patient Comfort
By minimizing the need for repeated tape application, Montgomery straps reduce skin irritation and pain, making them a more comfortable option for patients.
Tips for Ensuring Patient Satisfaction
Ensure that the straps have applied correctly and that the patient has informed about their purpose and how they work. Regularly check in with the patient to address any concerns or discomfort.
Maintaining and Caring for Montgomery Straps
Proper maintenance and care are essential for the longevity and effectiveness of Montgomery straps.
Cleaning and Sterilization
Montgomery straps should cleaned and sterilized according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This helps prevent infection and ensures that the straps remain effective.
When to Replace Montgomery Straps
Replace Montgomery straps if they show signs of wear, if the adhesive no longer sticks well, or if they become soiled. Regular replacement